Accelerating Climate Action: Why India's Rural Communities Hold the Key

On June 5th, people all over the world observe World Environment Day, a global day to spotlight the challenges faced by our environment, their impact on human progress, and focus on strategies and solutions to address them. Discussions on beating pollution, safeguarding the environment, limiting carbon footprints, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, tracking climate action, and achieving net-zero targets take center stage across the world. The past, present and future deliberations, all, revolve around the need for accelerated climate action in order to protect the most vulnerable communities from the poorest countries suffering the worst consequences of climate change.
Even as India commenced its G20 Presidency in December 2022, Prime Minister Narendra Modi dubbed Climate Change as one of the greatest challenges we face today. Prior to that, during the COP26 in Glasgow, PM Modi, introduced Mission LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment) advocating for increased action at the micro-level, on a day to day basis, by individuals, communities and organizations as part of an environment-conscious lifestyle; and that practitioners of such a lifestyle would be recognized as Pro Planet People. Both are important ideas to address climate change.
Environmental Stewardship at the Grassroots by Nurturing Rural Communities into Pro Planet People
Urban society, characterized by higher levels of population density, industrial infrastructure, economic activity, paying capacities, and consumption patterns, is perceived to be the main driver of global warming and climate change. Subsequently, a lot of climate change education, awareness creation and civic engagement pivots around aspects of urban life and livelihoods. Literacy, connectivity, networks, and access to resources in urban centers makes it easier for interest groups to mobilize urban communities for citizen action on climate change.
However, It is important to discuss how rural activities, which form the backbone of the Indian economy, also contribute significantly to environmental degradation and global warming.
Agriculture, practiced by nearly 60% of the rural Indian population, is largely a climate sensitive sector. On the other hand, it also contributes significantly to air, water and soil pollution. Its outcomes are invariably tied to the way in which this cause-effect cycle plays out. Excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, an unwelcome feature of modern day chemical farming, releases nitrogen oxides and ammonia into the air, soil and water, degrades soil quality, contaminates surface and groundwater, harms beneficial organisms and disrupts ecological balance.

Deforestation is another challenge that is worsening as more and more area is being brought under commercial cultivation, especially in the forest regions. While this is significantly reducing the earth’s ability to absorb carbon, it is also intensifying soil erosion which is leading to sedimentation in water bodies. Agriculture is also the biggest consumer of freshwater putting a severe strain on available freshwater resources, radically altering the local ecosystems including the earth’s drinking water supplies.
In many places across the country, agriculture is often accompanied by cattle rearing and dairy farming. Cattle are a major source of methane gas emissions; and improper management of animal wastes also contributes to environmental pollution in the rural belts. Moreover, when appropriate solid waste management practices and processes are still in a very formative stage in most Indian cities, rural areas only fare worse. All of these combined, and more, contribute to climate change. Addressing these challenges effectively not just requires but mandates active participation from rural communities as they not only rely heavily on natural resources for their livelihoods but are also hurt the most by the impacts of climate change.
More than 65% of the Indian population resides in rural areas and possesses immense potential to act as agents of change in countering climate change and helping India achieve the targets set under the Paris Agreement. Environmental consciousness on their part is vital for any decisive individual or community action at the grassroots in this direction. Civil Society Organizations (CSOs), like Bala Vikasa, have an important role to play in cultivating it.
Enabling Environment-Conscious Choices through Awareness, Education and Empowerment
Meaningful and sustained rural climate action is predicated upon communities being aware of what constitutes climate change, its root causes, and the practical implications of it on their own lives and livelihoods. For a majority of the rural population in India, whose access to both formal and informal education has been quite limited and/or delayed, topical information about climate change is largely absent from the public sphere. Even the environment-positive practices that have been part of the communities’ cultural and traditional practices for the better part of their history are sometimes not viewed, appreciated, or promoted as simple, yet promising, countermeasures to climate change.

Introducing this discourse - compartmentalized, simplified, and contextualized to different community groups/stakeholders and mapped with specific community-level actions, greatly helps in educating them on the drivers of climate change, catalyzing behavior change, and engaging them in localized, bite-sized mitigation and adaptation measures. Bala Vikasa’s Community-Driven Development programming provides a few examples in this regard.
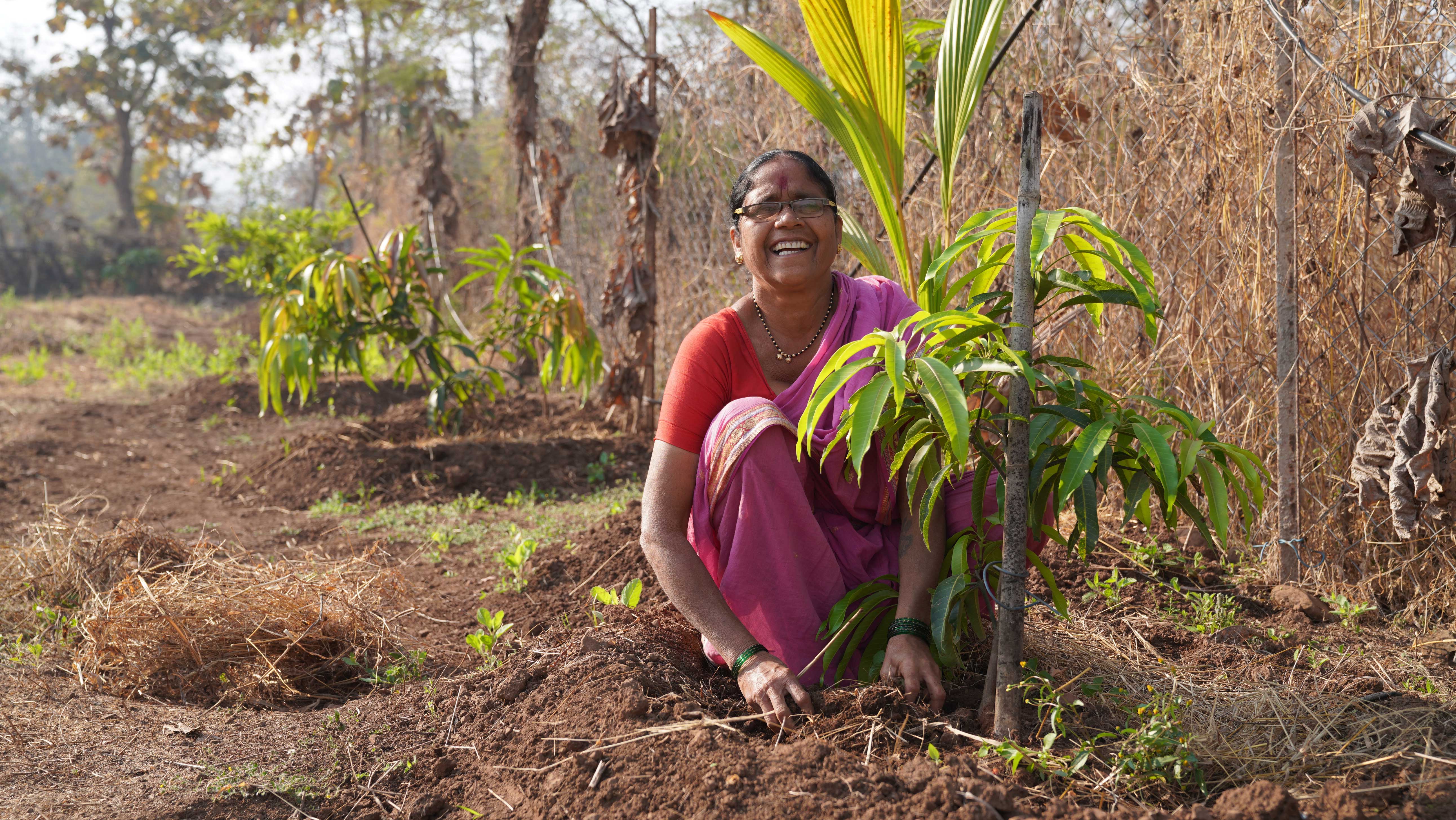
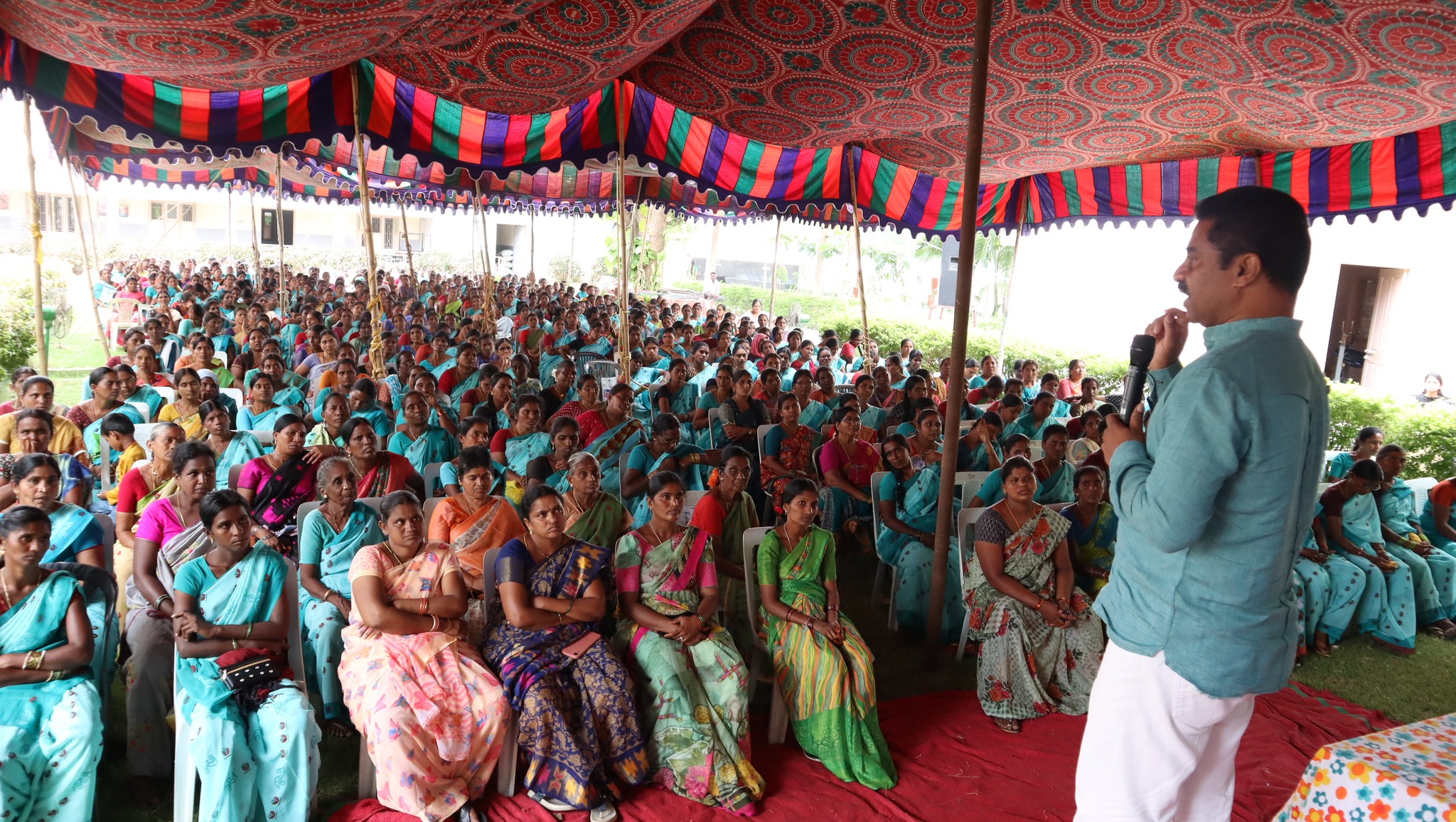
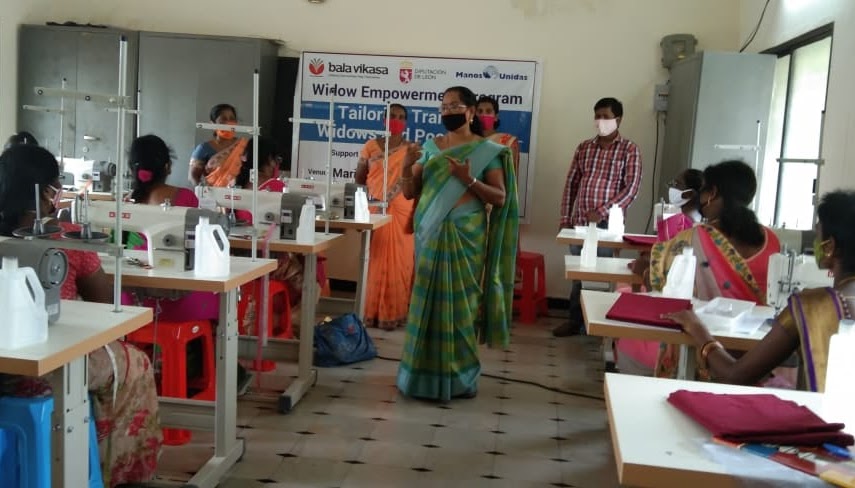
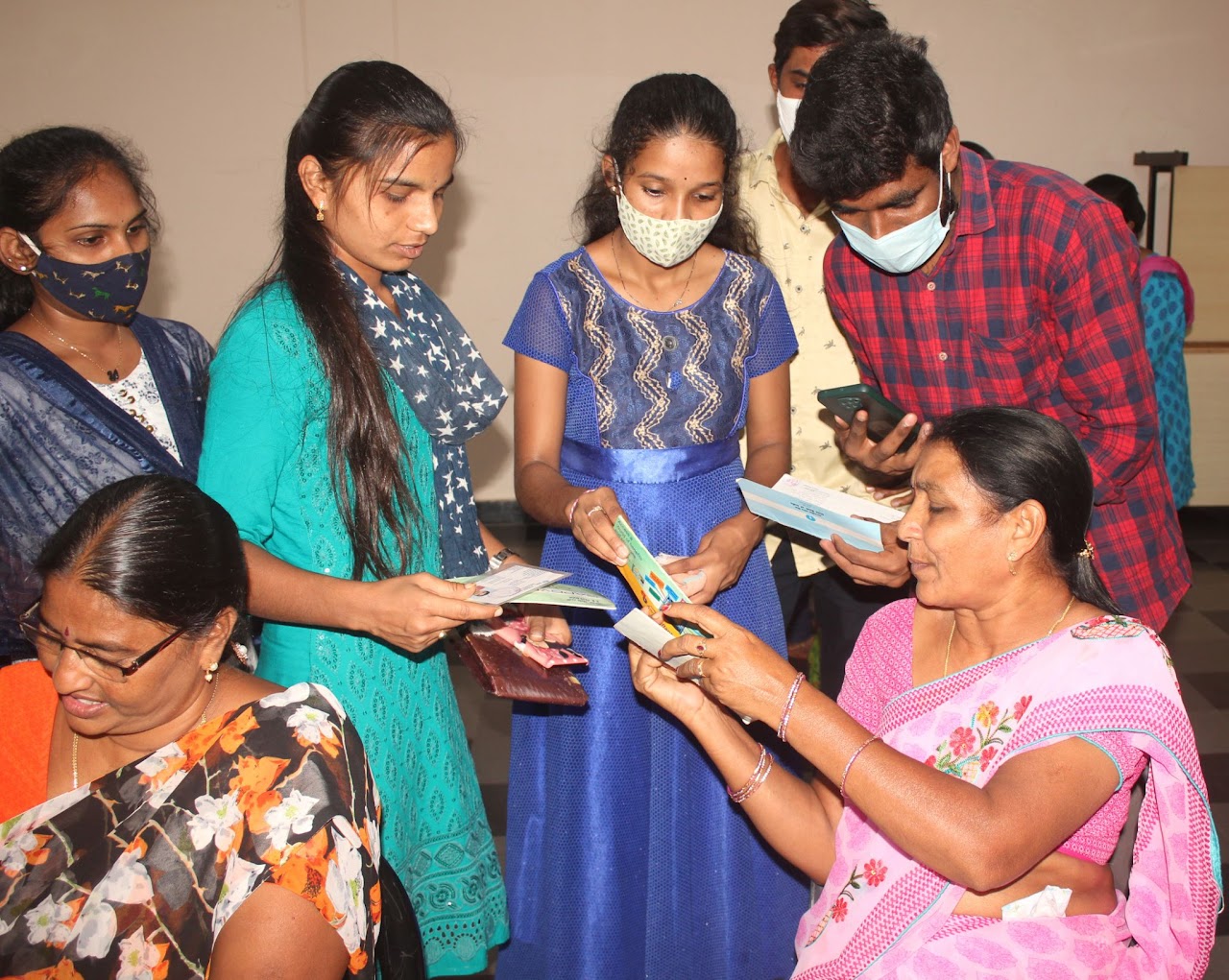
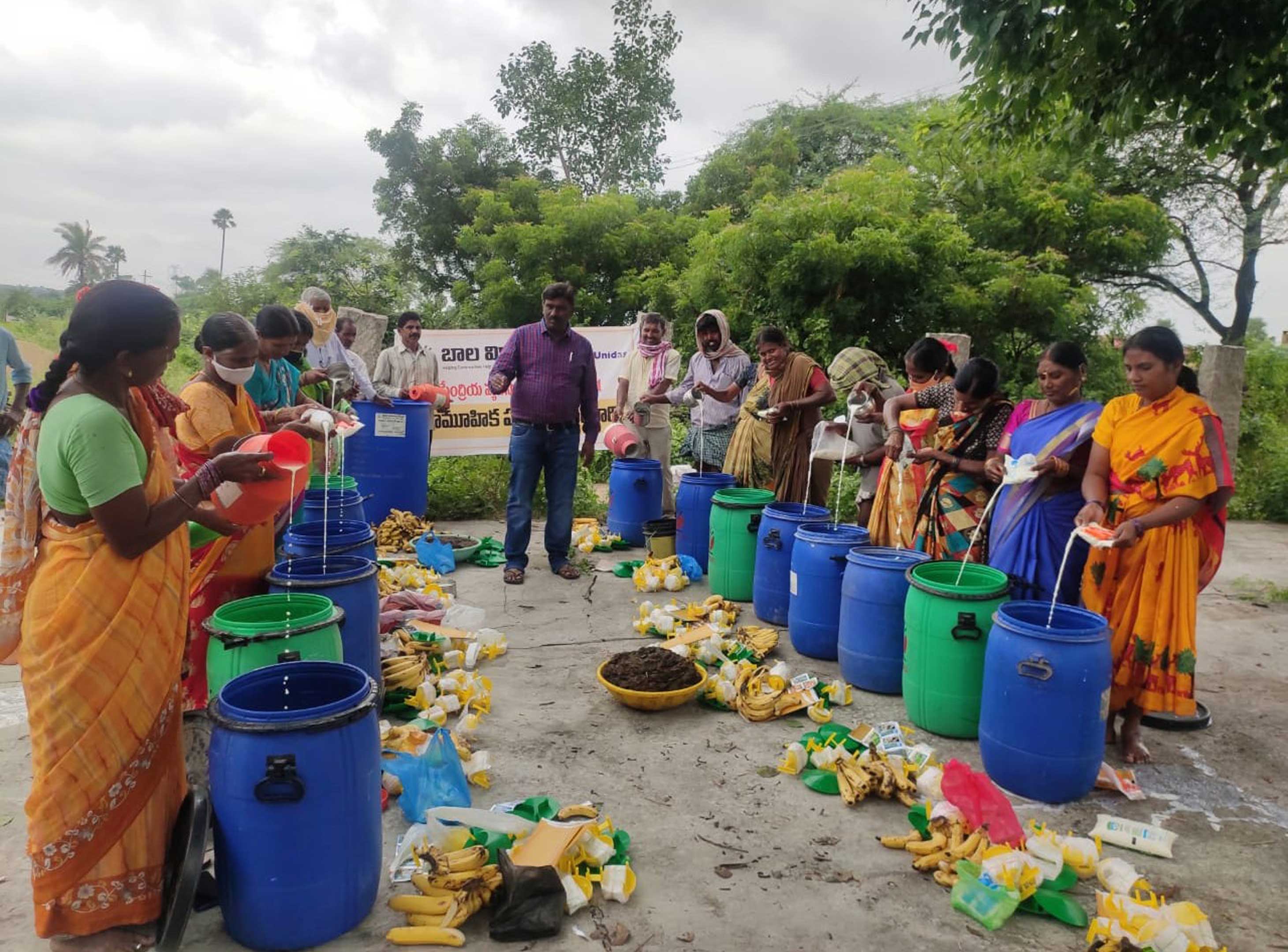
There are about 23,000 women savings groups (SHGs) operating under Bala Vikasa as part of its Women Integrated Development Program aimed at empowering rural poor women intellectually, financially, socially, and politically. The environment is an important topic for discussion during their monthly meetings and yearly capacity-building programs. Information on the importance of plantation in their villages, benefits of organic farming practices and farm ponds, measures to reduce environmental pollution, etc., is shared with them intensively. Later on, these women are encouraged to spearhead plantation activity at both the household and community level, take up organic farming practices in their own farms, work towards maintaining proper sanitation and hygiene through village development committees, and so on.

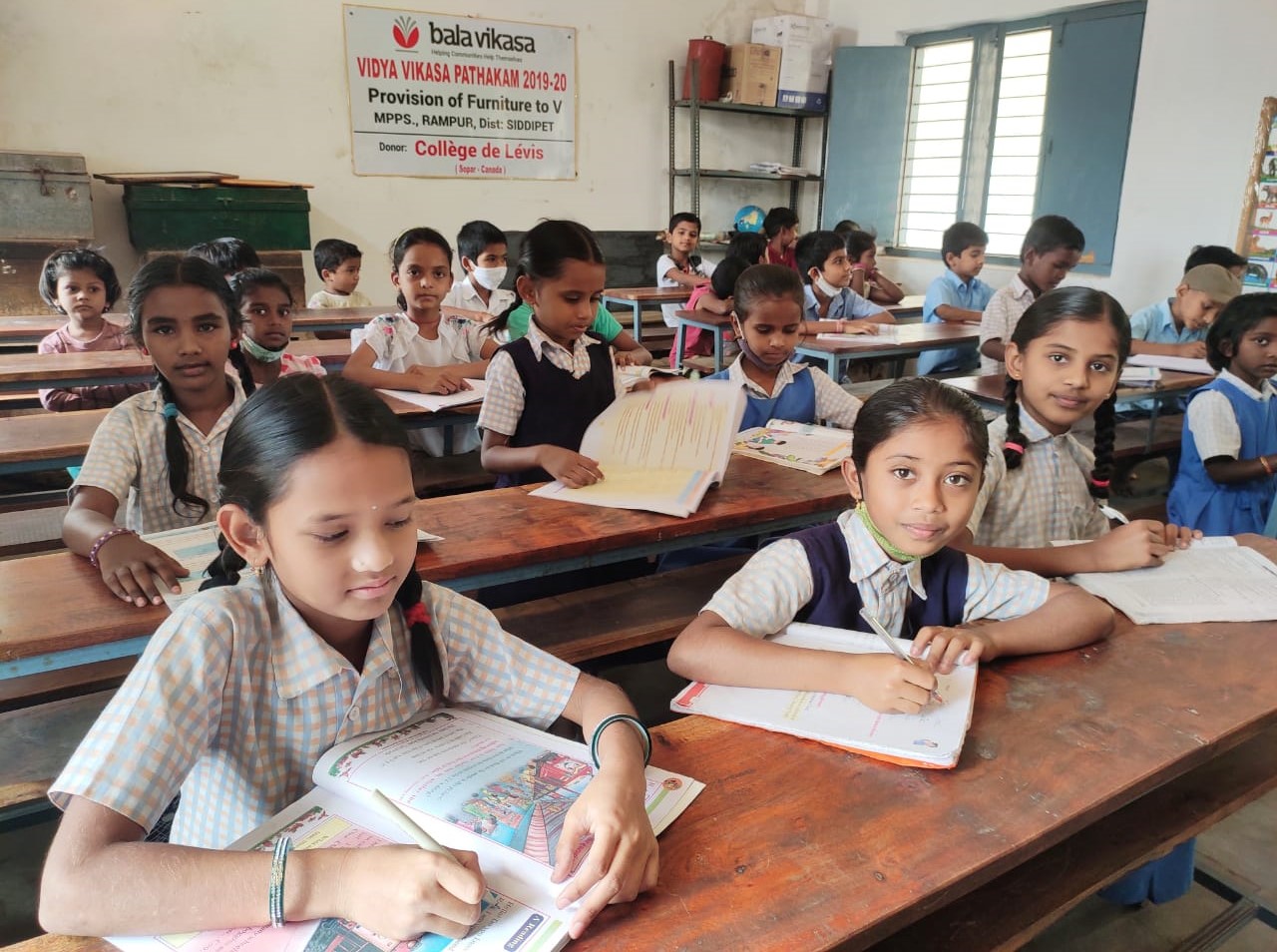
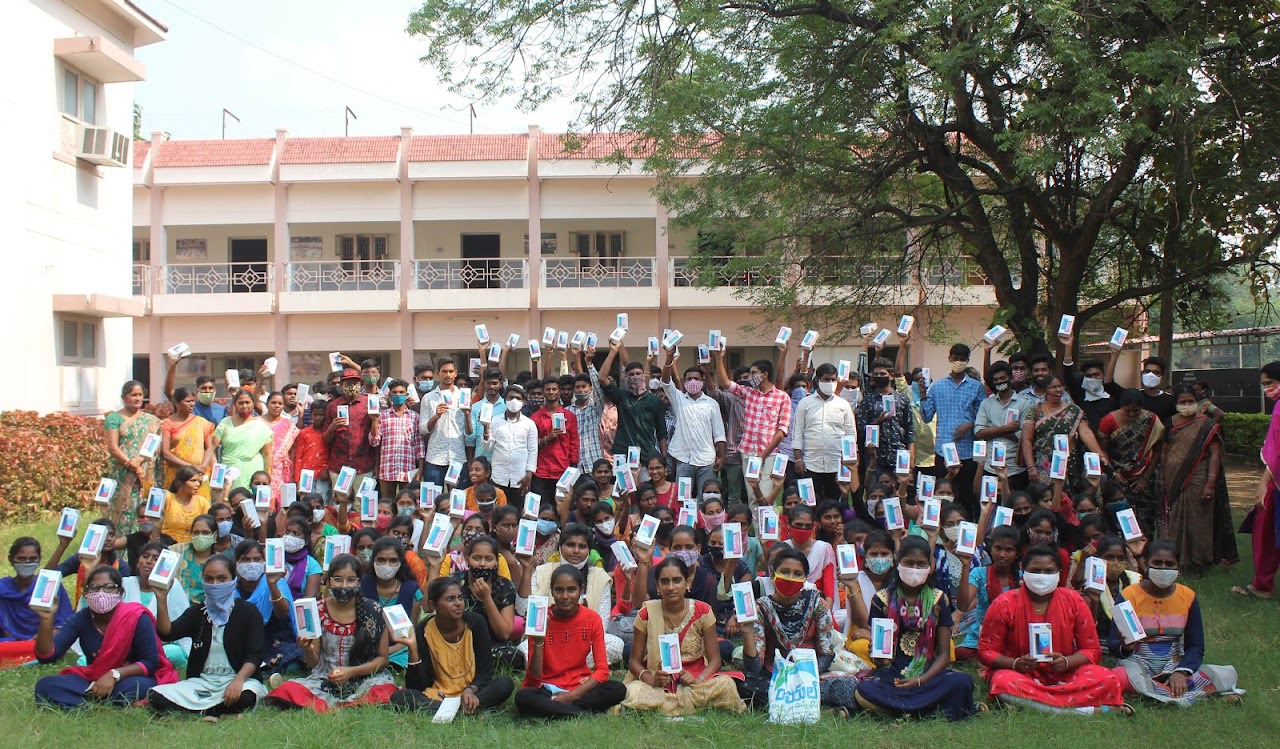
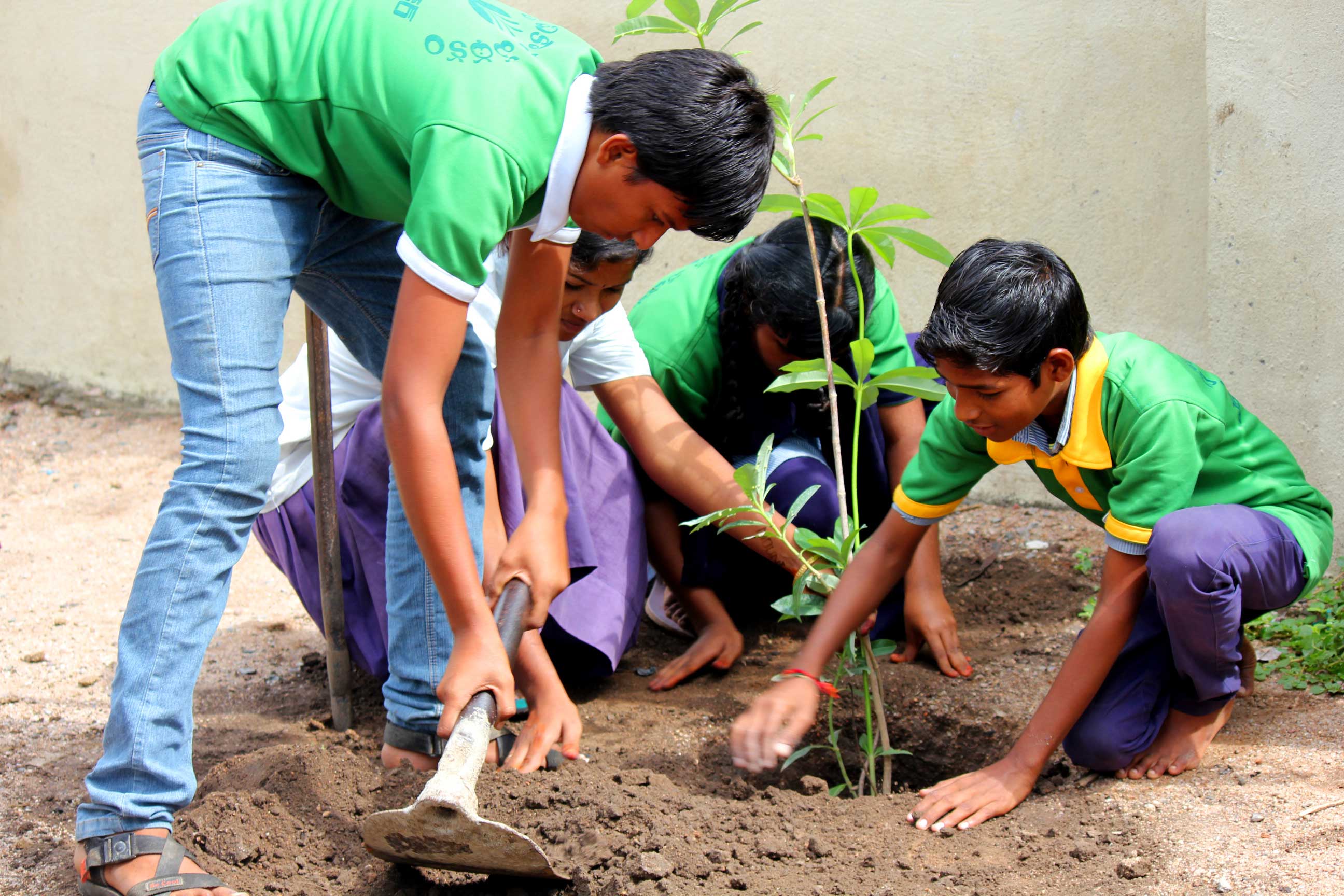
In another program that seeks to deliver quality public education by bridging infrastructural and technical gaps, Bala Vikasa formed student-based eco clubs in about 550 rural government schools, where the poorest children come to study. An important aspect of programming is the incentivization of schools with infrastructure like furniture, and mini-libraries, on the condition that the school, led by its student committees, maintains cleanliness and hygiene in the school premises, utilizes various garbage disposal utilities appropriately, ensures proper management of solid and liquid wastes and conducts needed plantation activities regularly. Based on the school’s satisfactory performance on these indicators over a 24-month period, Bala Vikasa approves the incremental grant of furniture, libraries and digital classrooms. The core belief around this approach is that the environmental consciousness cultivated in the young minds would hold great promise for a sustainable future, way beyond the prescribed activities at the school incorporated to instill collective responsibility and ownership of the assets.

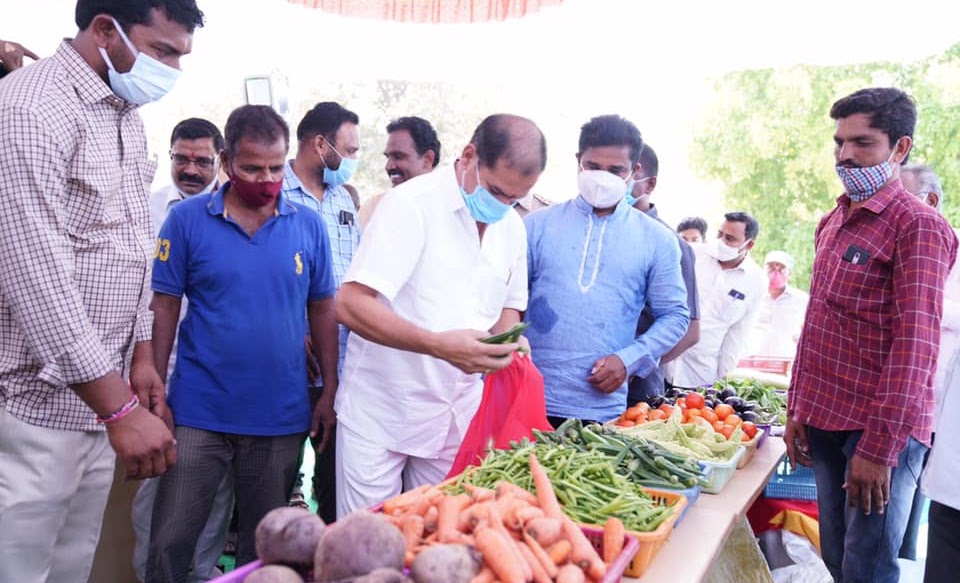
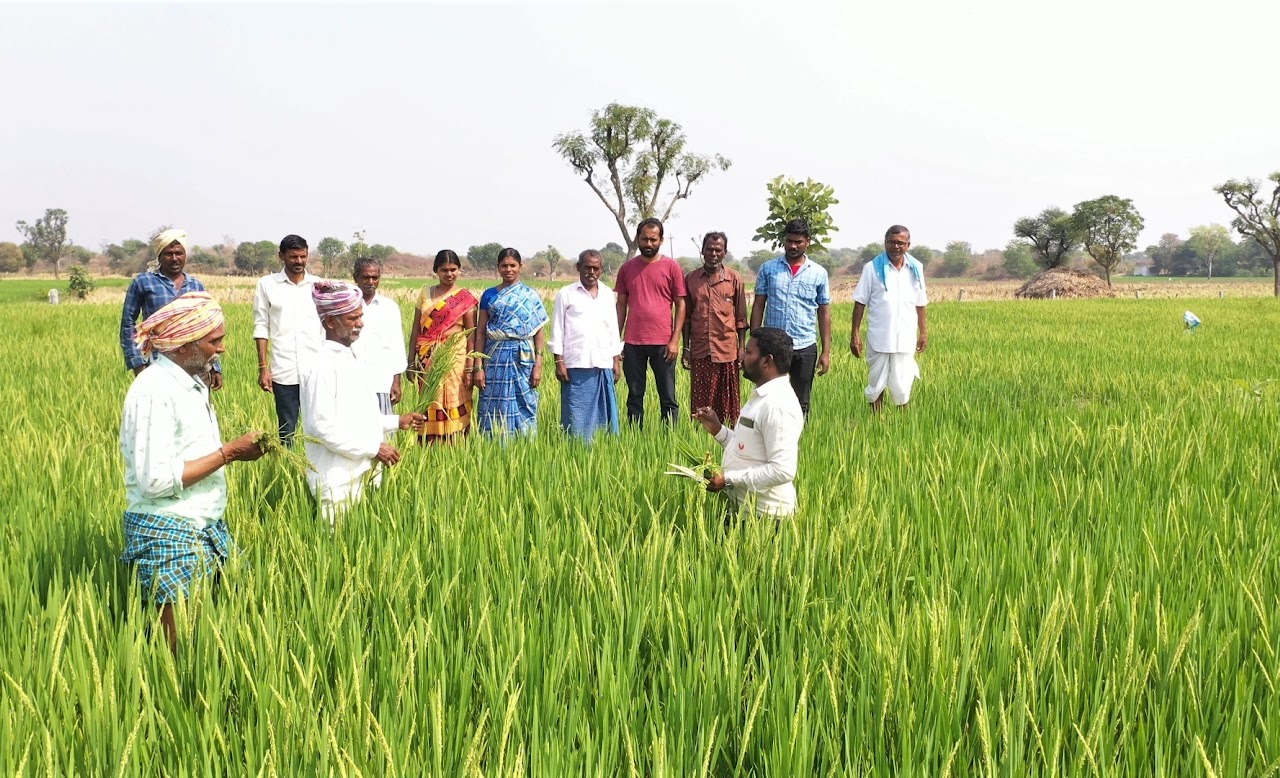
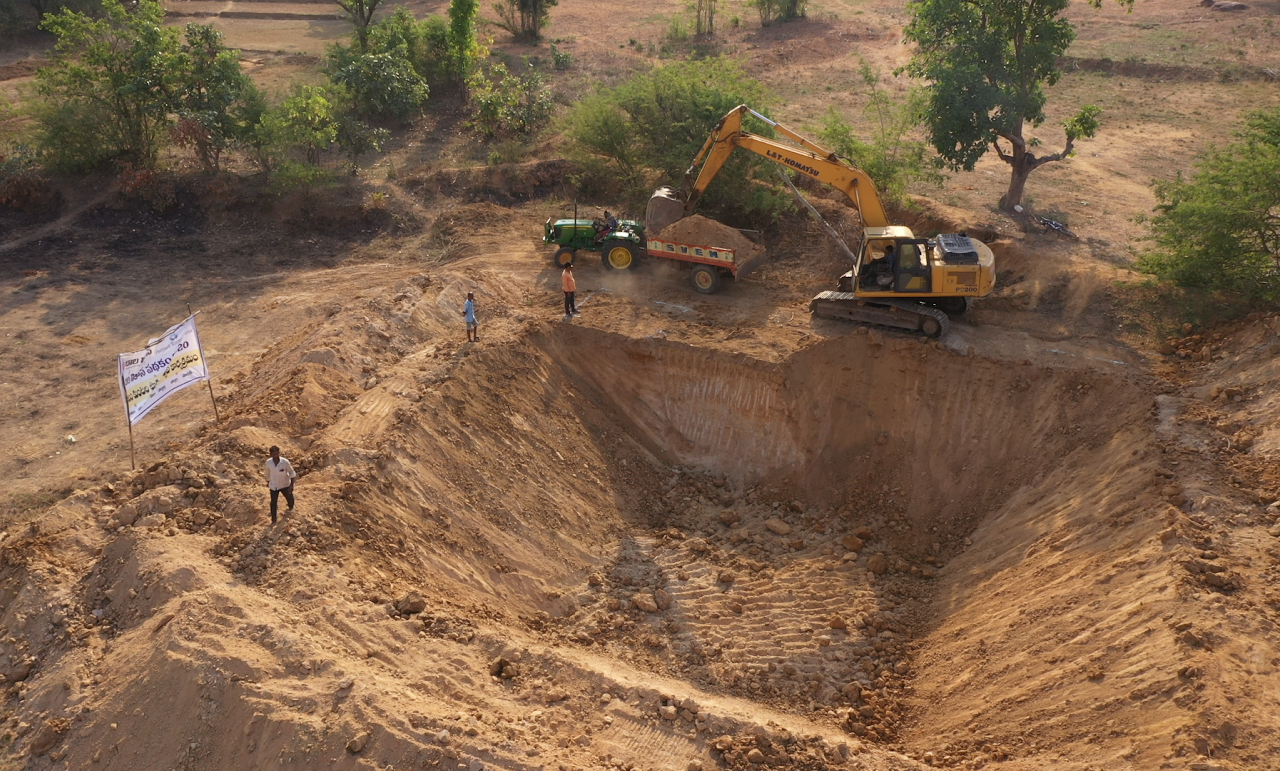
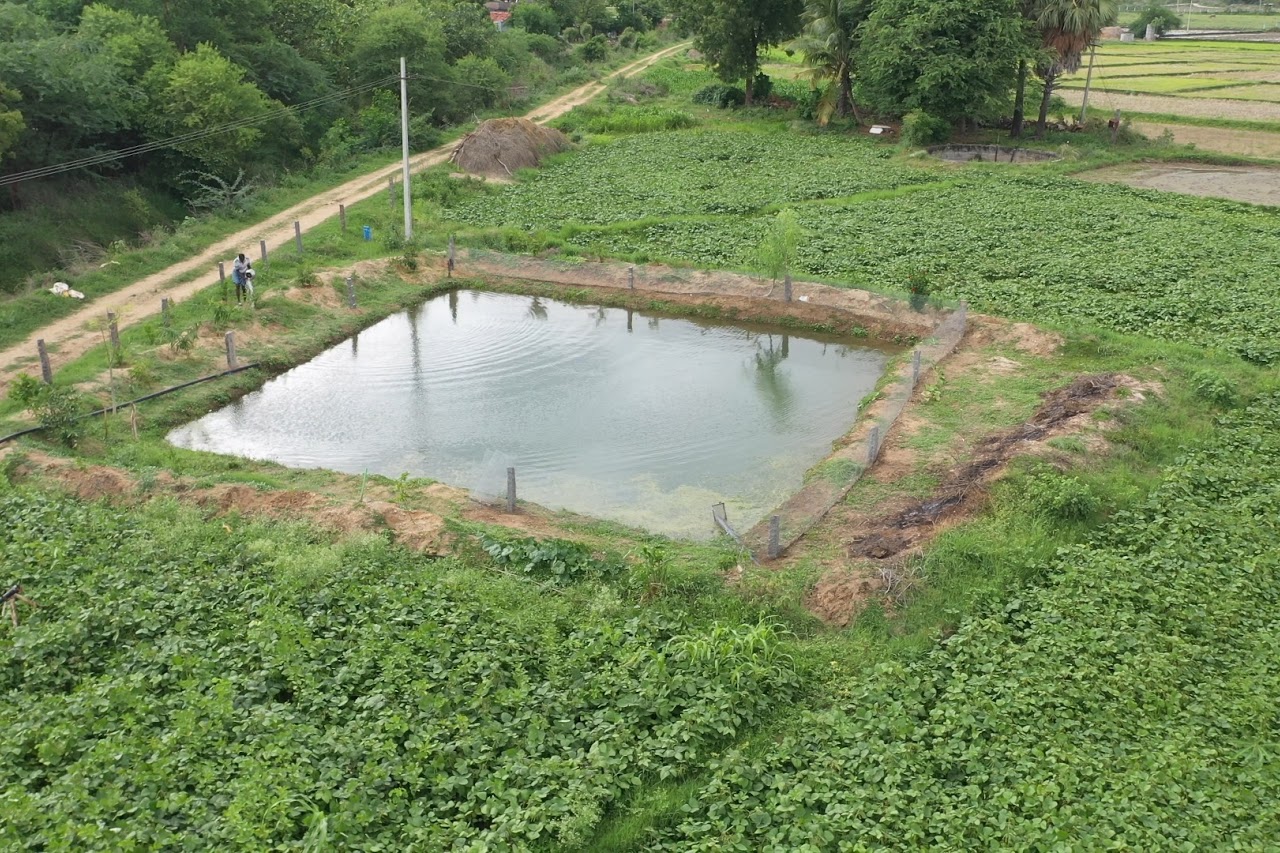
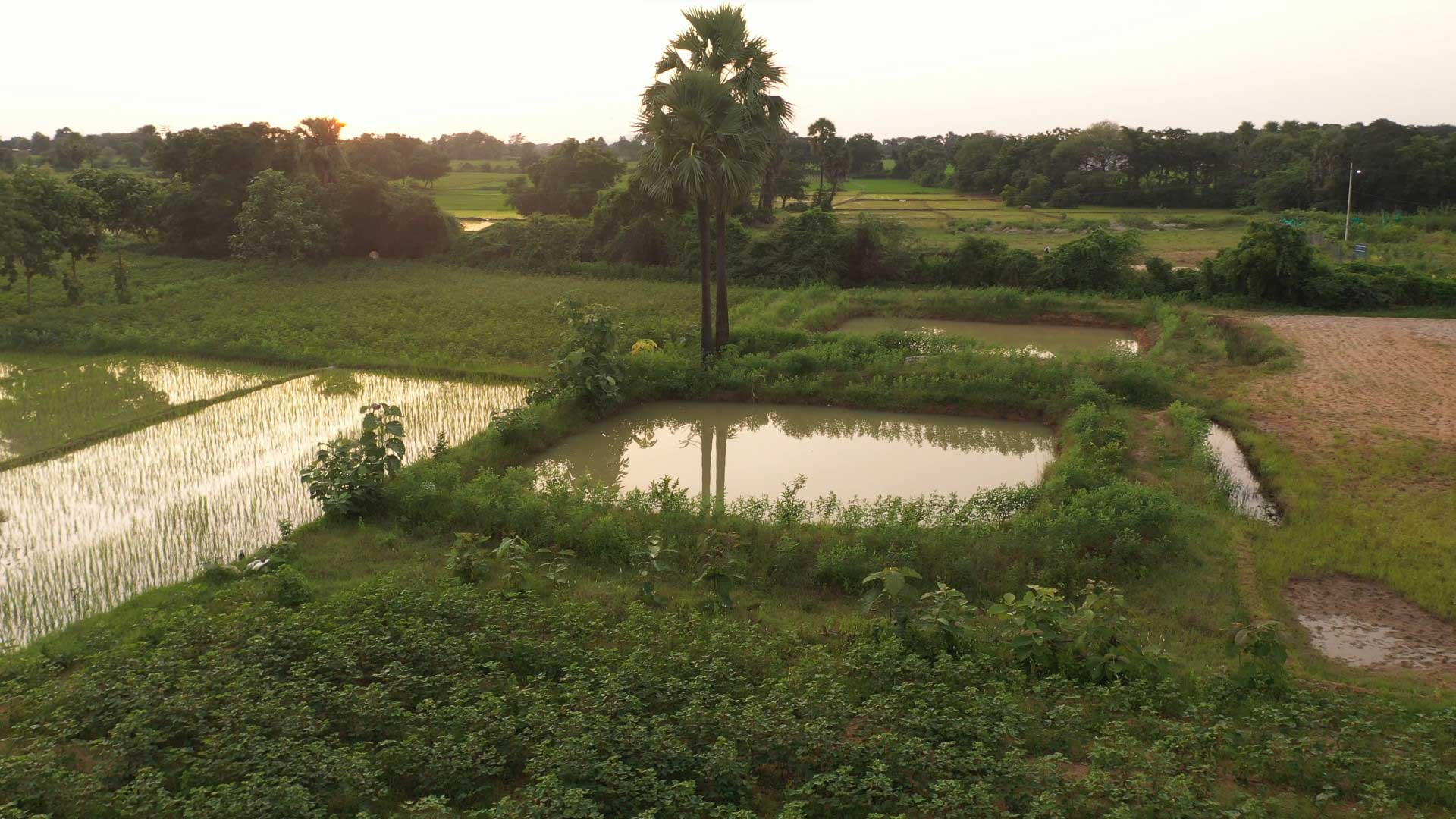
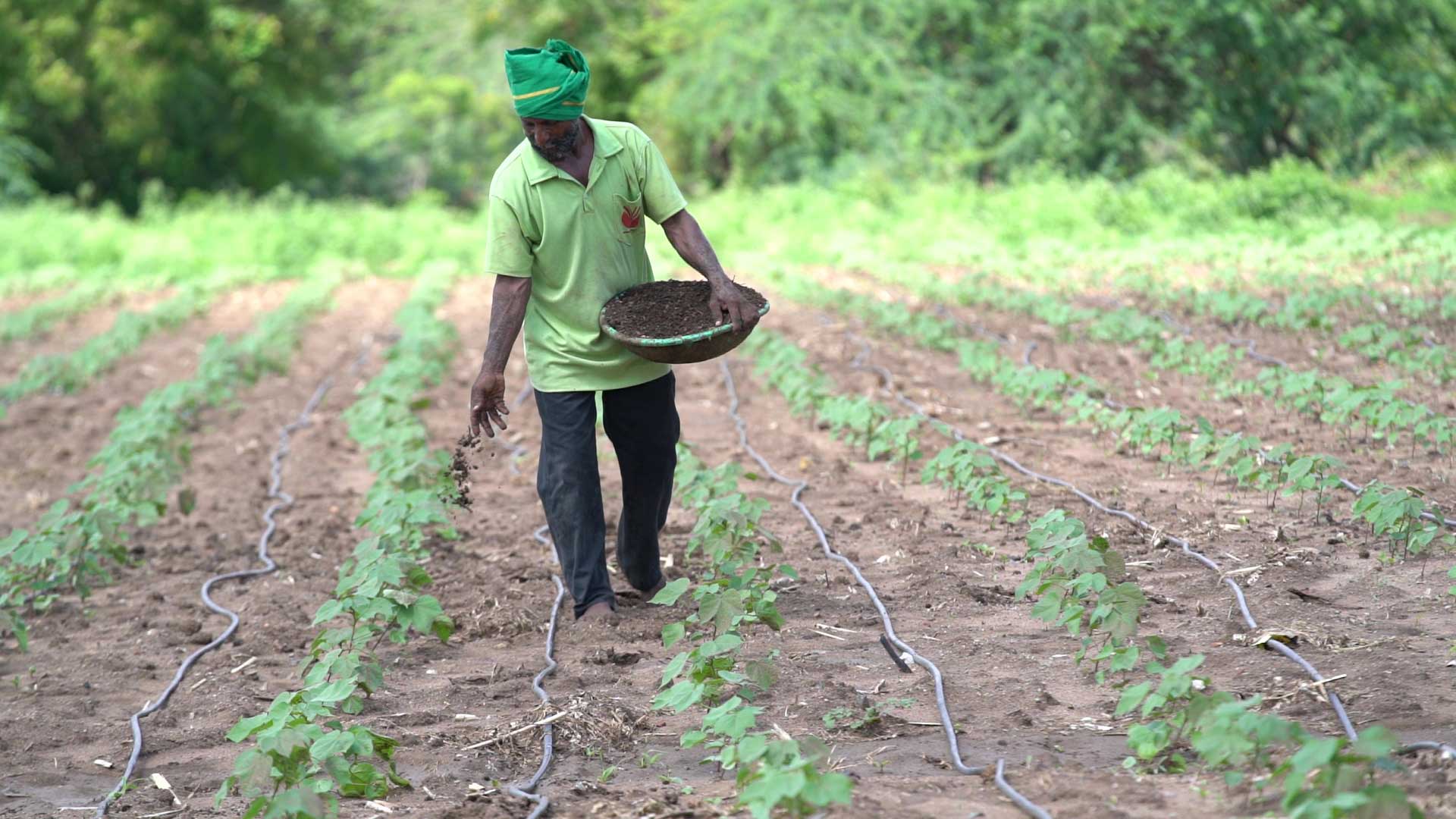
Similarly, farmers are being educated on the environmental impacts of activities such as chemical farming and the intensive usage of freshwater for agriculture, and the need for their active participation in ensuring food and water security for generations to come. Consequently, about 75,000 farmers have been engaged in community-led watershed activities like tank desiltation and construction of farm ponds, and 1500+ farmers are engaged in organic farming. Intensive awareness creation and knowledge sharing in the form of special-purpose Grama Sabhas, technical capacity-building sessions, exposure visits, and dissemination of instructional manuals and IEC materials on different sustainable agricultural practices and their socio-economic benefits driven by today’s consumer behaviors, helped in motivating farmers for necessary action.
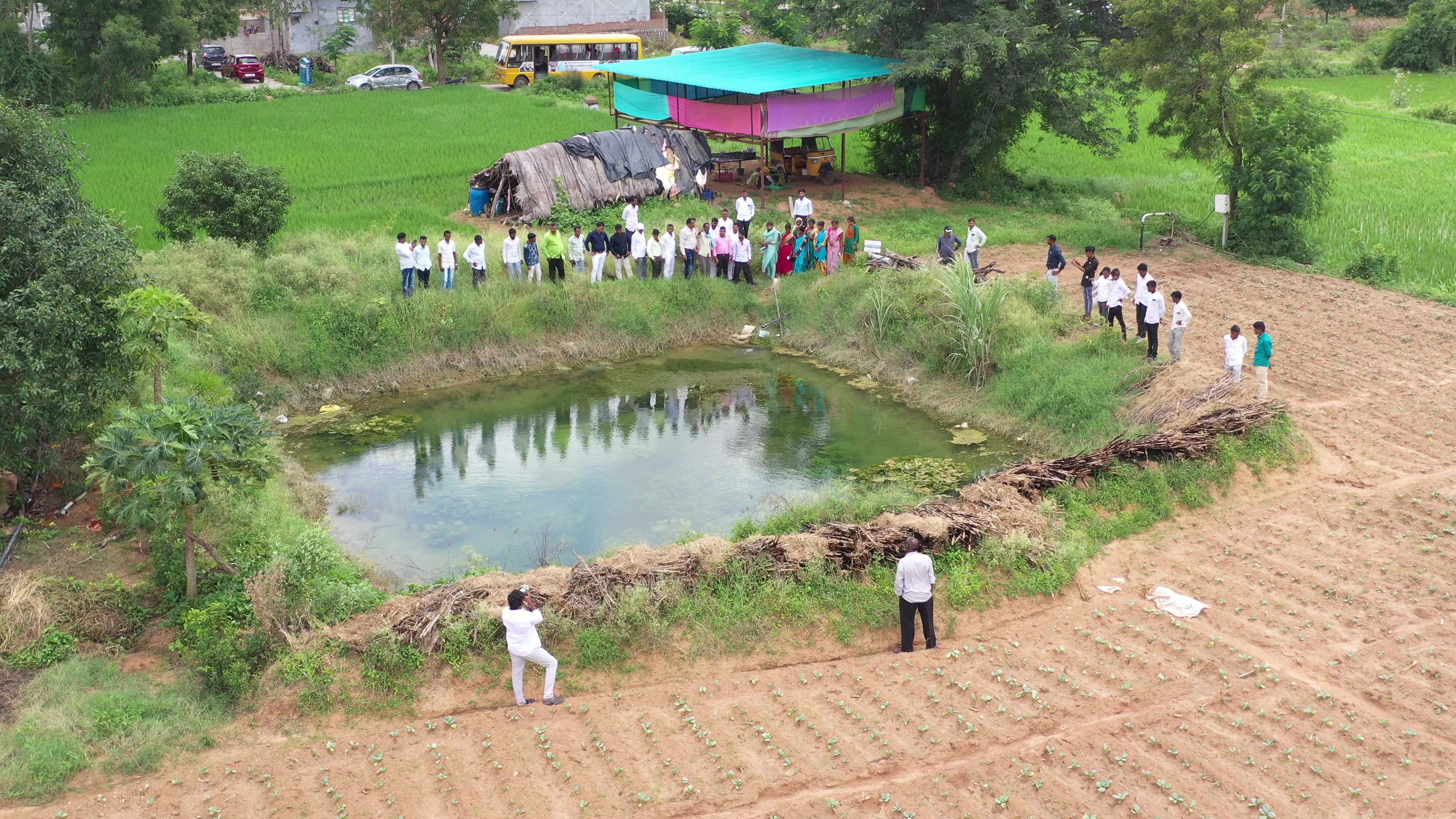

Some of the combined results of the aforementioned efforts are the plantation of about 10 Lakh saplings by rural women in 1600+ villages significantly increasing the village green cover, construction of 32,000+ household soak pits to manage wastewater effectively, annual water savings of approximately 1 TMC through farmer-led conservation projects, and 1000+ acres of farmland under organic cultivation. This goes to demonstrate the massive potential of environmentally-conscious rural communities in championing high-impact, micro-level actions that strike at the heart of rural climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts.
While there are, without doubt, certain imposing inhibitors to community-level action in the rural heartlands, the fact that these communities are so intimately linked to the environment for their survival and well-being presents a window of opportunity to motivate and mobilize them as powerful agents of change and sustainability advocates. The same is reinforced in Bala Vikasa’s Five Year Strategic Plan 2020-25 which places a big thrust on anchoring ‘environmental consciousness’ in all actions steering Community-Driven Sustainable Development.Further, Bala Vikasa Center for Social and Responsible Business (CSRB) is actively supporting social startups working in the areas of climate change, plastic recycling, waste management, etc.
India’s rural communities will have a key role to play in tackling plastic pollution, biomass burning, clean energy adoption, biodiversity preservation and many such issues, and their success would largely depend on how various development actors recognize their potential, support their involvement and inspire action.